The Comprehensive Guide to Tympanometry: Understanding Middle Ear Health
The middle ear plays a crucial role in our ability to hear, acting as a bridge between the outer ear and the inner ear. When the middle ear is not functioning properly, it can lead to hearing difficulties, discomfort, and even long term complications. Tympanometry is a diagnostic tool that evaluates the health and function of the middle ear, helping identify issues such as ear infections, fluid buildup, and eustachian tube dysfunction.
What is Tympanometry?
Definition and Purpose
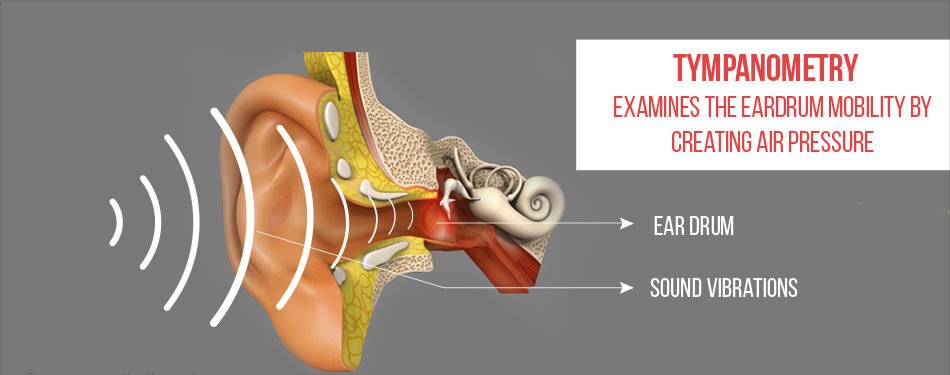
Tympanometry is a quick, noninvasive test that measures the movement of the eardrum (tympanic membrane) in response to changes in air pressure. It evaluates the health and function of the middle ear, including the eardrum and the ossicles (tiny bones that transmit sound). The primary purpose of tympanometry is to diagnose middle ear conditions that may affect hearing.
Why is Tympanometry Important?
1. Diagnosis of Middle Ear Disorders: Tympanometry helps identify conditions like ear infections, fluid buildup, and eustachian tube dysfunction.
2. Assessment of Eardrum Function: It evaluates how well the eardrum moves in response to sound and pressure changes.
3. Complementary to Audiometry: Tympanometry is often performed alongside other hearing tests, such as pure tone audiometry, to provide a comprehensive assessment of hearing health.
4. Early Detection: Early diagnosis of middle ear issues can prevent complications and improve treatment outcomes.
How Does Tympanometry Work?
The Tympanometry Process
1. Preparation: The test is performed by an audiologist or hearing care professional. You will be seated comfortably, and the audiologist will explain the procedure.
2. Probe Insertion: A small, soft probe is placed in the ear canal. The probe contains a speaker, microphone, and air pressure regulator.
3. Air Pressure Changes: The probe changes the air pressure in the ear canal, causing the eardrum to move back and forth.
4. Measurement: The microphone records the eardrum’s movement, and the results are displayed on a graph called a tympanogram.
5. Analysis: The audiologist interprets the tympanogram to assess middle ear function and identify any abnormalities.
What Does a Tympanogram Show?
A tympanogram is a graph that plots the eardrum’s movement against changes in air pressure. The shape and peak of the graph provide valuable information about middle ear health:
Type A: Normal eardrum movement, indicating healthy middle ear function.
Type B: Flat or reduced eardrum movement, suggesting fluid buildup or eardrum perforation.
Type C: Negative pressure in the middle ear, indicating eustachian tube dysfunction.
Who Should Get a Tympanometry Test?
Signs You May Need a Tympanometry Test
Persistent ear pain or discomfort.
Hearing loss or muffled hearing.
Frequent ear infections.
Feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear.
Difficulty equalizing ear pressure (e.g., during flights or diving).
History of middle ear issues or surgeries.
AtRisk Groups
1. Children: Tympanometry is commonly used to diagnose middle ear issues in children, as they are more prone to ear infections and fluid buildup.
2. Individuals with Hearing Loss: Tympanometry helps determine if hearing loss is due to middle ear problems.
3. People with Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: Those with conditions like allergies or sinusitis may benefit from tympanometry.
4. PostSurgery Patients: Tympanometry is often used to monitor middle ear function after surgeries like tympanoplasty.
Benefits of Tympanometry
1. Quick and Painless: The test takes only a few minutes and is completely noninvasive.
2. Accurate Diagnosis: Tympanometry provides precise information about middle ear function.
3. Early Detection: Identifying middle ear issues early can prevent complications and improve treatment outcomes.
4. Comprehensive Hearing Assessment: When combined with other tests, tympanometry offers a complete picture of hearing health.
5. Improved Treatment Planning: The results help audiologists recommend appropriate treatments, such as medications, surgery, or hearing aids.
What to Expect During a Tympanometry Test
Before the Test
Avoid inserting anything into your ears (e.g., cotton swabs) before the test.
Inform your audiologist about any ear pain, infections, or recent surgeries.
Be prepared to discuss your medical history and any symptoms you are experiencing.
During the Test
You will be seated in a quiet room.
The audiologist will insert a small probe into your ear.
You may feel slight pressure changes in your ear, but the test is painless.
The test typically takes 23 minutes per ear.
After the Test
The audiologist will discuss the results with you and explain what they mean.
If abnormalities are detected, further testing or treatment may be recommended.
Common Conditions Diagnosed by Tympanometry
1. Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection)
Otitis media is a common condition, especially in children, characterized by fluid buildup and inflammation in the middle ear. Tympanometry helps diagnose and monitor the condition.
2. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
The eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the throat and helps regulate air pressure. Dysfunction can lead to negative pressure in the middle ear, causing discomfort and hearing issues.
3. Perforated Eardrum
A hole or tear in the eardrum can affect hearing and increase the risk of infections. Tympanometry helps assess the extent of the damage.
4. Otosclerosis
Otosclerosis is a condition where abnormal bone growth in the middle ear affects hearing. Tympanometry can help identify this condition.
5. Cholesteatoma
A cholesteatoma is an abnormal skin growth in the middle ear that can cause hearing loss and infections. Tympanometry helps detect this condition.
Tympanometry for Children
Why is Tympanometry Important for Children?
Children are more susceptible to middle ear issues due to their developing anatomy and frequent colds. Tympanometry is a valuable tool for diagnosing and monitoring conditions like otitis media, which can affect speech and language development.
How is Tympanometry Performed on Children?
The procedure is the same as for adults, but the audiologist may use childfriendly techniques to ensure cooperation. Parents are often present during the test to provide comfort and reassurance.
The Future of Tympanometry
Technological Advancements
1. Portable Tympanometers: Compact, handheld devices are making tympanometry more accessible, especially in remote areas.
2. Digital Tympanometry: Advanced digital systems provide more accurate and detailed results.
3. Integration with Telehealth: Remote tympanometry is becoming possible, allowing patients to receive hearing care from the comfort of their homes.
Personalized Hearing Care
Advancements in tympanometry are enabling more personalized and precise diagnoses, ensuring that each individual’s unique needs are met.
Common Myths About Tympanometry
Myth 1: Tympanometry is Painful
Fact: Tympanometry is a quick, noninvasive, and painless procedure.
Myth 2: Only Children Need Tympanometry
Fact: Tympanometry is beneficial for individuals of all ages, especially those with middle ear issues.
Myth 3: Tympanometry is Only for Severe Hearing Loss
Fact: Tympanometry can detect even mild middle ear problems that may not yet cause noticeable hearing loss.
Myth 4: Tympanometry is Not Accurate
Fact: Tympanometry is a highly accurate and reliable diagnostic tool when performed by a certified audiologist.
Conclusion
Tympanometry is an essential diagnostic tool for evaluating middle ear health and function. Whether you’re experiencing ear pain, hearing loss, or other symptoms, a tympanometry test can provide valuable insights and guide effective treatment. With advancements in technology and the convenience of portable devices, taking care of your hearing health has never been easier. Don’t wait—schedule a tympanometry test today and take the first step toward better hearing and overall well being.